Category: Medicine & health
Clear cell renal cancer is the most common form of kidney cancer, with approximately 1 000 new cases in Sweden every year. If the disease is not detected before it spreads to other parts of the body, the prognosis is bleak. Only 10 per cent of these patients survive five years...
As we become increasingly better at designing and producing different nanomaterials, the question of how this affects our environment and our health arises. What are the risks of, for instance, nanofibre ‘dust’ in connection with the production of new materials and products? Nanoparticles are invisible to the naked eye, but...
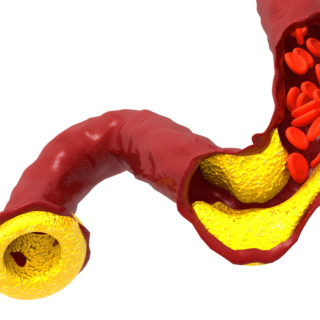
“The most common cause of death and the most disabling illness worldwide is plaque in the blood vessels which, if they rupture, can lead to a heart attack or a stroke”, says Isabel Gonçalves, Professor in cardiologist at the Clinical Research Centre in Malmö. “However, today there is really only...
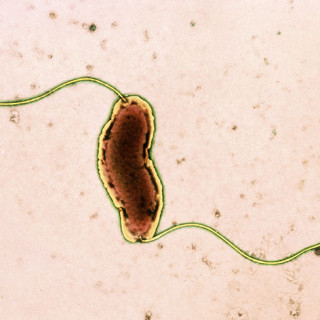
Bacteria as an organism All things now living on Earth belong to one of the three main groups called Bacteria, Archaea and Eukaryotes (all plants and animals are included here). The organisms we commonly call bacteria belong to the group bacteria or archaea. Bacteria are usually small, approximately one micrometre,...
According to a new analysis from AgriFood Economics Centre focusing on the economic impact of five common foodborne diseases, the costs associated with food poisoning in Sweden exceed SEK 1 billion per year. That’s nearly SEK 500 million more than previously estimated. A STUDY published 2015 at the AgriFood Economics...
Opinion by Inga Odenholt, Professor of Infectious Diseases with a deep committment to the issue of rational use of antibiotics and reduced antibiotic resistance. Today there are bacteria resistant to all known types of antibiotics, and it has become increasingly difficult for the pharmaceutical industry to develop new solutions. Almost...
Research is already underway on how the breast milk protein HAMLET can be used to treat cancer. Findings from Lund University indicate that it may even kill two types of respiratory bacteria. At the same time, the protein can make partially resistant bacteria – which every year claim many lives...
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria mean that the infections that we usually regard as minor become more complicated or even life-threatening. Infected wounds don’t heal; pneumonia can lead to death. Microbiologists Tobias Olofsson and Alejandra Vásquez see living bacterial cultures, which produce lots of different antibiotic substances, as a solution to the problem....
Researchers at Lund University and others have shown that skin pigments convert UV radiation into heat through a speedy chemical reaction that blasts protons from the pigment molecules. The skin pigment thereby protects the body from hazardous UV radiation from the sun. Researchers at Lund University, together with colleagues in...